Indexing for Performance
Types of Indexes
B-Tree Index
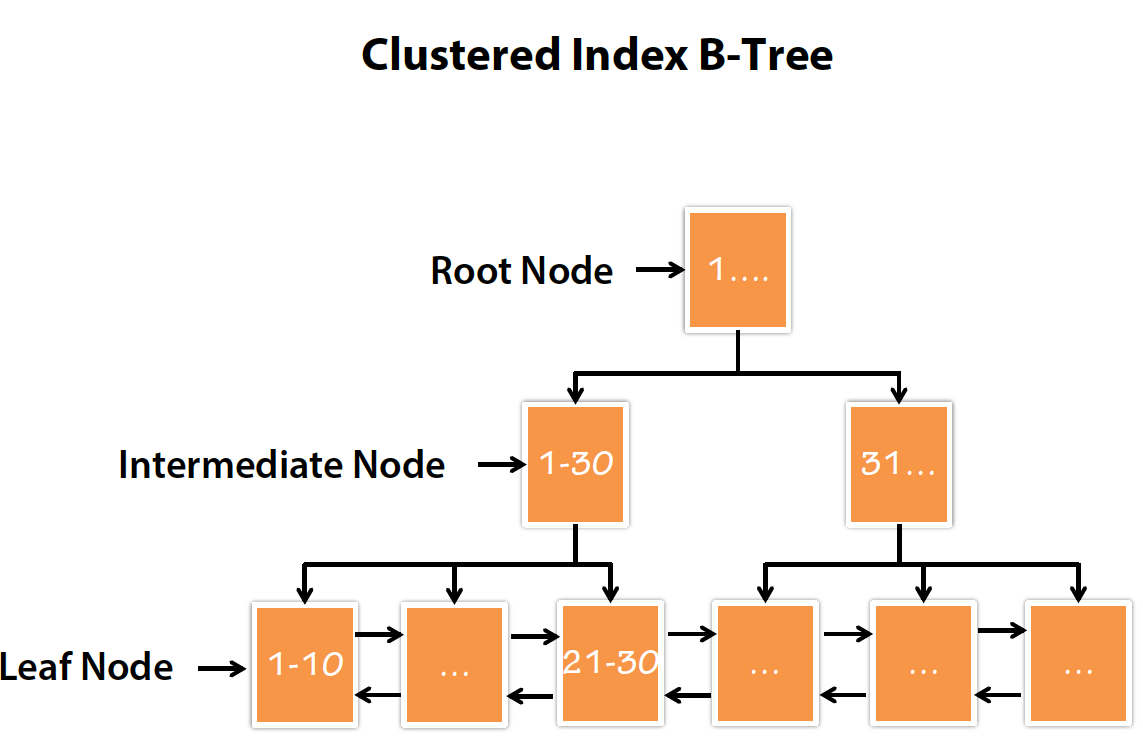
When you hear in the industry the word index, they often mean a B-tree index. Most of the MySQL storage engine supports B-tree indexes. In B-tree index, each leaf node contains a link to the next node for the fast range traversal. All the values are stored in order and each leaf page is at the same distance from root level.
B-Tree index is often referred as an index
Most storage engines support B+TreeIndexEach Leaf node contains a link to the next node for the fast range traversals
Values are stored in order
Each leaf page is at the same distance from root level
InnoDBstorage uses B+TreeIndex
Advantages of B-Tree Index
- B-Tree Index speeds up data access
- Increase performance of following query patterns :
- Full Value (e.g 'Jseph', 'Peruzal')
- Leftmost Value or Colum Prefix (e.g 'Per' from 'Peruzal')
- Range of Value (e.g from 1 to 99 or 'Joseph' to 'Prudence')
- B-Tree supports helps ORDER BY clause to increase performance
Clustered Index for InnoDB
- Leaf pages contains full rows
- Node pages contains indexed columns
- Clusters data by Primary Key
- If not Primary Key –uses Unique NonnullableIndex
- If no Unique NonnullableIndex –create hidden Clustered Primary Key
Travesing B-Tree Index
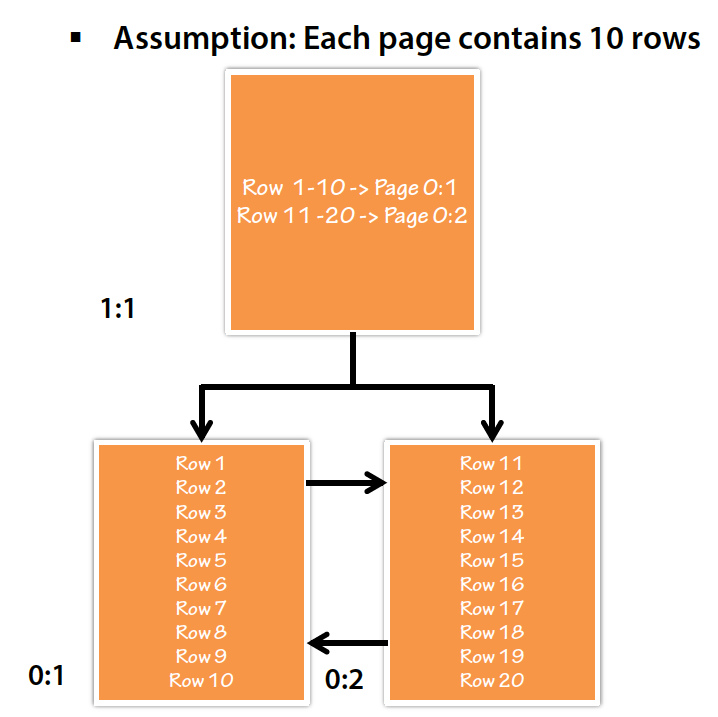
Assuming each page contains 10 rows of data