Declaring a Class
Syntax
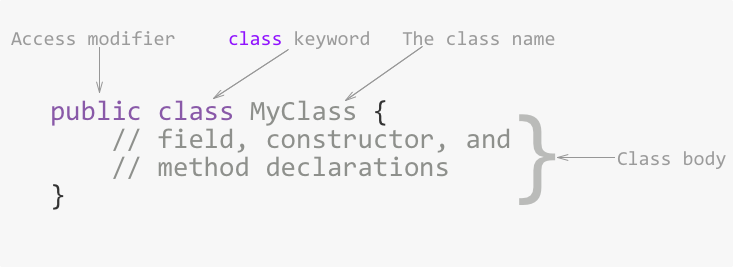
This is the bare minimum required when declaring a class. It contains the required components to declare a class.
Access Modifiers
Are special keywords used to control where the class and its members can be used.
| Modifier | Package | World |
|---|---|---|
| public | Y | Y |
| protected | Y | N |
| no modifier | Y | N |
| private | N | N |
The access modifiers controls who have access to the class, for classes this is generally public. public means the class is accessible to any other classes. Its fully accessible to the world.
The class keyword then follows, and then the name of the class.
In Java, the name of the public class should be the same as its file name.
Example
The following declares a class called LightBulb, with four member variables. The class will live in a file calledLightBulb.java.
public class LightBulb {
float voltage;
float price;
String type;
boolean state;
}
Declare a Cat class with three member variables. Color is another class already defined in the java.awt package, we are re-using without recreating the same functionality. We use the import statement to bring the Color class into the Cat class declaration. File name will be Cat.java
import java.awt.Color;
public class Cat {
String name;
Color color;
float age;
}
Here is another example of what a chat message class might look like in our Android Mobile Group Chat App later on in the course. File name will be Message.java
import java.util.Date;
public class Message {
long messageId;
int type;
String author;
String message;
Date createdAt;
}
We have defined a Message class, that have five fields. Since the Date class is already defined we imported it into our class. The Date class is defined in the java.util package.