Defining Interfaces
An interface is defined with the interface keyword, followed by the interface name and then the body.
Example
Here is how the Listener interface is defined in the Emitter class we will be using to when receiving messages from the chat server in our program.
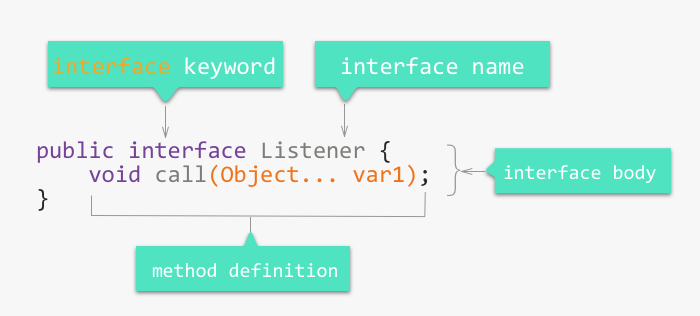
It will be our responsibility to define what happens in the call method when we receive the message from the server. We have to provide the implementation.
Interface Fields
All fields in an interface are constants by default. We could have created an interface to provide configuration information to our program as follows :
Example Interface Fields
interface Config {
String API_URL = "http://chat.peruzal.co.za"; //constant
String DEFAULT_USER = "guest"; //constant
}
The API_URL and DEFAULT_USER are constants although we have left the static and final keyword modifiers.
The public, static and final modifiers are redundant since all fields are automatically constants.
The full definition for DEFAULT_USER is as follows :
interface Config {
//public, static and final are redudant
public static final String DEFAULT_USER = "guest";
}
Interface Methods
Methods in the interface only provide definitions. It is illegal to provide the definition unless the method is marked default.
Example Interface Method Defintion
This is how the call method is definied in the Listener interface. Notice the method does not have a body,(opening and closing curly braces, s {}).
void call(Object... var1);